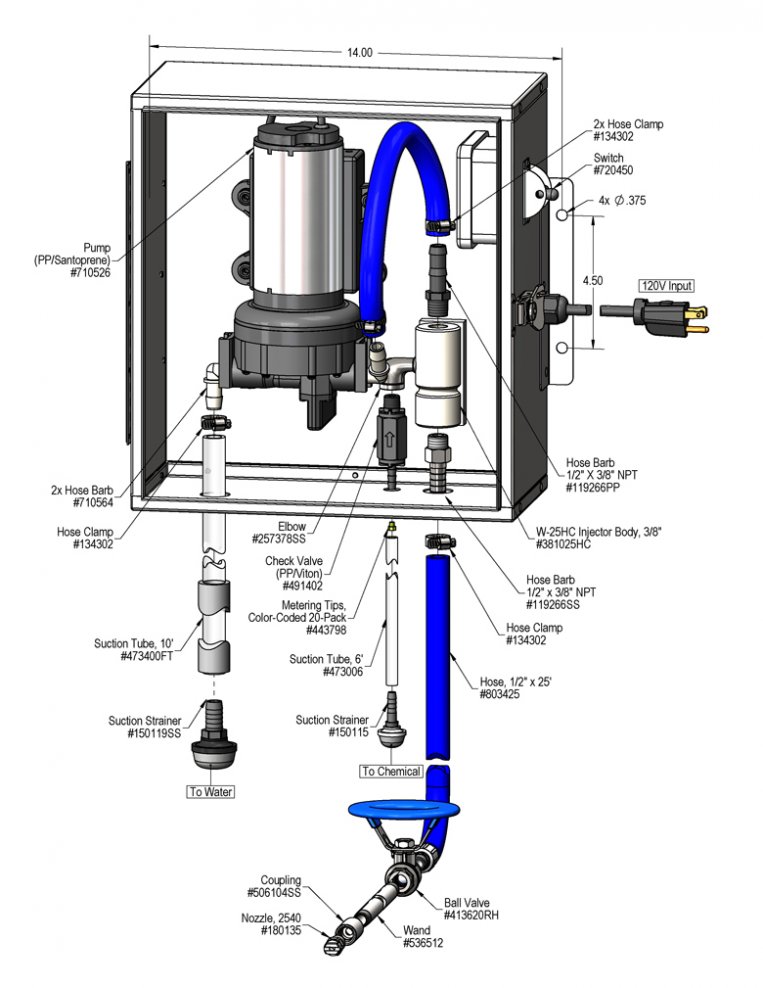
Overview
The Electric W-25 Asphalt Release Sprayer is a spray applicator for diluting and spraying asphalt release chemicals on to truck beds or tools to prevent asphalt from sticking. Designed for facilities with low or no water pressure. An electric pump draws water from a static tank and provides the water pressure to power a venturi injector. The injector draws chemical concentrate from any container and blends it into the water stream to create an accurately diluted solution using precision metering tips. The solution is then projected through the discharge hose, wand and fan nozzle.