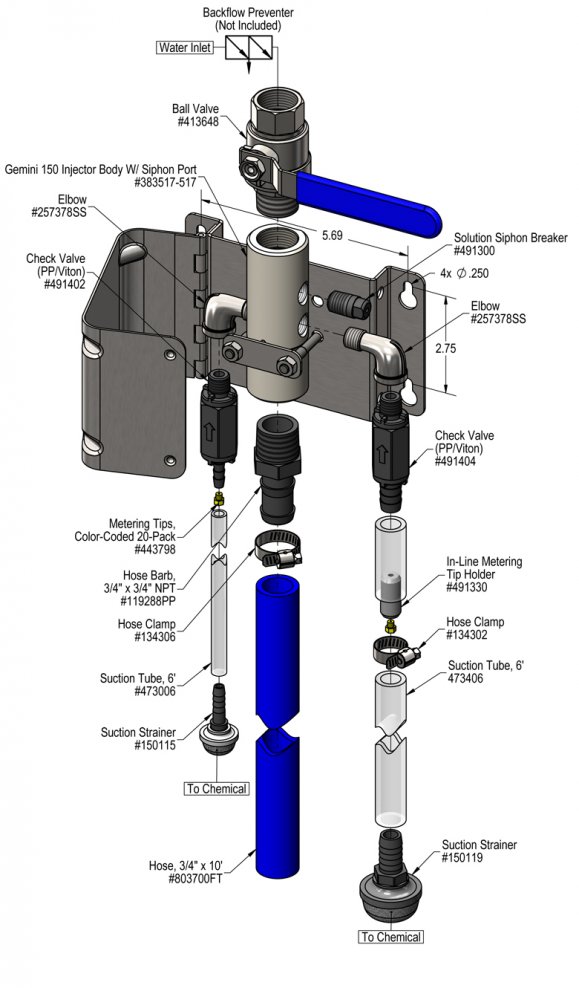
TO SET DILUTION RATIO, thread a color-coded metering tip into each tip holder. See chemical labels for dilution ratio recommendation or consult your chemical supplier.
- For the strongest dilution ratio do NOT install a colored metering tip.
- The dilution ratios in the metering tip chart are based on water thin chemicals with a viscosity of 1CPS. Thicker chemicals will require a larger tip than the ratios shown in the chart.
- Chart shows ratios at 40 PSI water pressure. Actual water pressure is shown on unit gauge during operation. Adjust metering tip selection based on actual water pressure using the online Metering Tip Calculator or the math formula shown in the chart.
- Select and thread the tip color that is closest to your desired chemical strength into the tip holder. DO NOT OVER-TIGHTEN
- Application results will ultimately determine final tip color selection.
- Push the chemical tubes over the tip holders and place the strainer in the chemical concentrate.
- If necessary, cut suction tube(s) to length.
If a leaner solution than the maximum shown in the chart is required, it will be necessary to use one proportioner to pre-dilute the concentrate, and a second to dilute the resulting solution to the required final ratio. If this Double Dilution procedure is required, choose two metering tips whose ratios, when multiplied together, result in a ratio that is as close as possible to the required final ratio. Example: For two "Bottle Fill" Mixing Station valves with 40 PSI water pressure, use a White Tip (37:1) and a Corn Yellow Tip (21:1) to achieve a final solution ratio of 777:1.