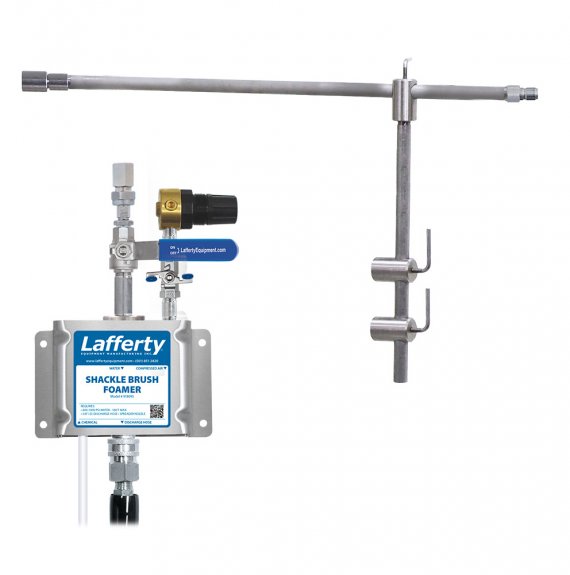
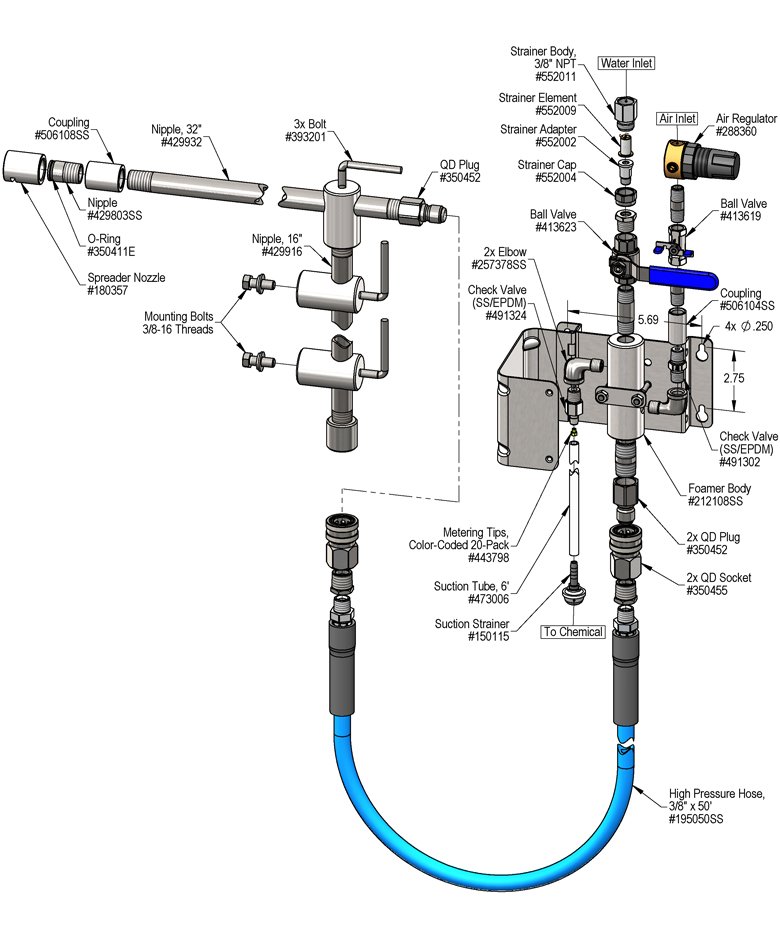
Overview
The Shackle Brush Foamer is a low volume foam applicator for projecting foaming chemicals down into shackle brush cabinets. This stainless steel venturi injection system uses high water pressure (400 - 1000 PSI) to draw and blend chemical concentrate into the water stream to create an accurately diluted solution. Rich, clinging foam is created by injecting compressed air into the solution to greatly increase volume and coverage ability. Foam then flows through the discharge hose, adjustable arm and Spreader Nozzle™ – and is projected into the brushes.