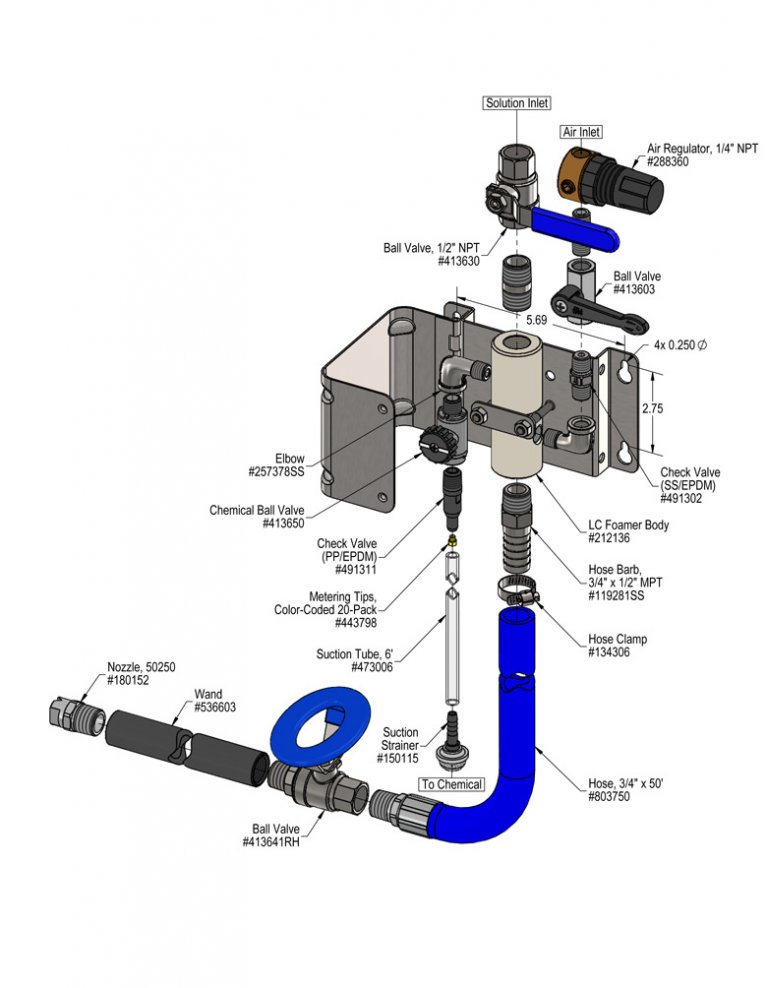
Overview
The Pump Fed LC Foamer with Chemical Ball Valve receives pressurized chemical from a user-supplied chemical pump and the venturi injection system draws a second chemical into the first to create an accurately blended two-chemical solution. Rich, clinging foam is created by injecting compressed air into the solution to greatly increase volume and coverage ability. A medium volume of foam is produced and projected through the discharge hose, wand and fan nozzle onto any surface at distances up to 12 feet.